L'Oréal's share price has thus lost 11% since the start of the year, and is now back on the EUR 400 mark. This contraction follows a banner year, during which the share jumped 35% to reach an all-time high of EUR 461.85. By 2022, the company had already suffered, losing 20% of its value. By contrast, over the previous ten years, the share had seen only annual increases (even excluding dividends), as the following table shows:

Less dynamic sales growth
Against these high standards, investors are disappointed. And with good reason: the share was already trading at EUR 400 in August 2021, three years ago. The market's disaffection with L'Oréal has coincided with a slowdown in sales growth. The chart below illustrates annual sales growth over the last 12 quarters.

A situation acknowledged by L'Oréal's CEO, at an event organized by J.P. Morgan at the end of June. Nicolas Hieronimus indicated that the Group had revised its growth forecasts for the cosmetics market downwards. Growth in the sector is likely to be between 4.5 and 5% this year, mainly due to China.
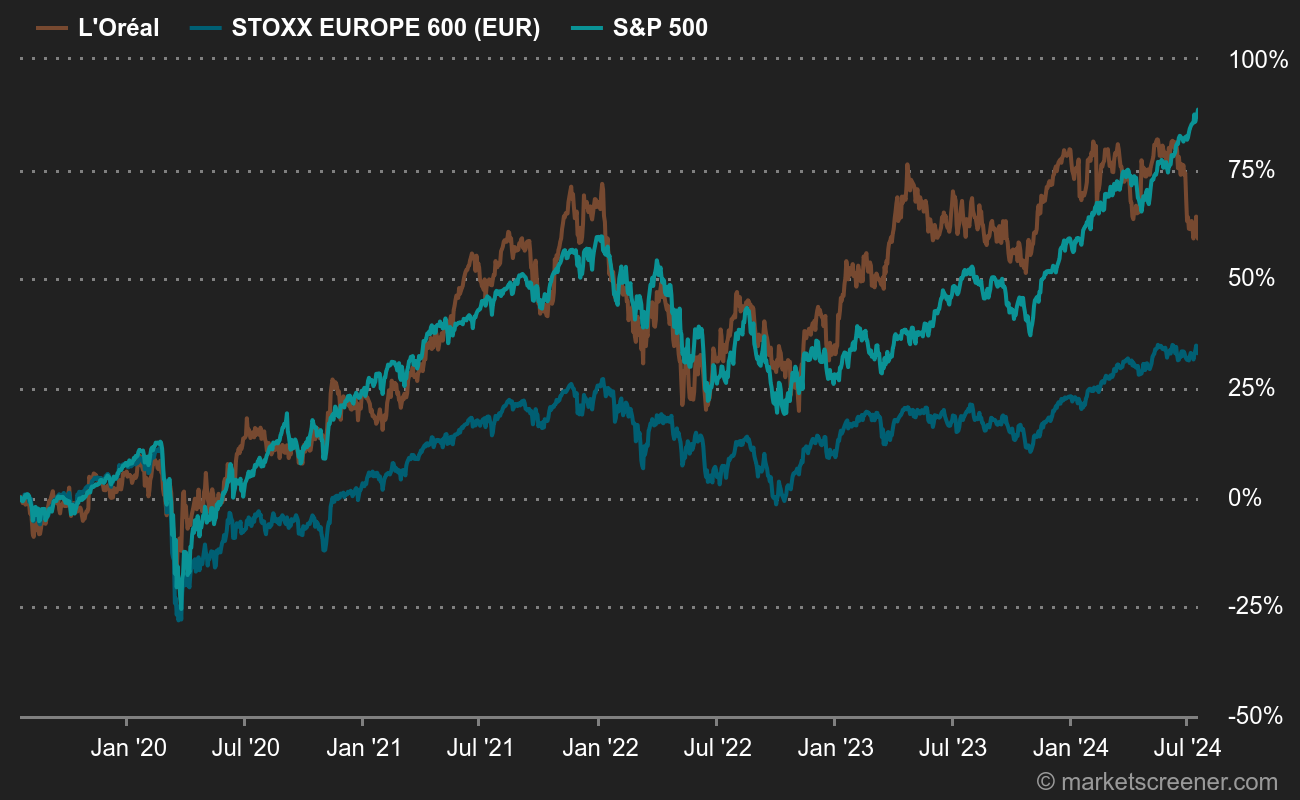
The share price has clearly fallen lately
"The global beauty market is slowing down after three years of strong growth. Extra-normal price growth is fading, the US mass/derme markets are slowing down, and China remains anemic, the lack of acceleration in the second half of the year in this market having led to L'Oréal's recent downward revision of market growth", explains Jefferies' sector analysis team, who believe that the problem will not be limited to the short term. "If market growth slows to the long-term average of 4-4.5%, we believe this poses a risk to consensus growth forecasts and valuation, particularly for market leader L'Oréal", warns the research house. This is because, in addition to the underlying trend in these major markets, the sector leaders are facing competition from small, long-toothed entrants who are nibbling away at market share.
Caution is therefore called for, especially if the Chinese market continues to falter due to restrictive Western trade policies.

 By
By 




